Different COVID-19 Vaccines
Share
The pandemic of COVID-19 has demonstrated the need for preventive medicine to a great extent. We all know now that merely dealing with symptoms and prognosis of a disease, be it acute or chronic, infectious or non-communicable, is not going to get us any benefit in the long run. What really matters is timely prevention and the right measures so we can deal with the symptoms in time. One important element in this regard is vaccination.
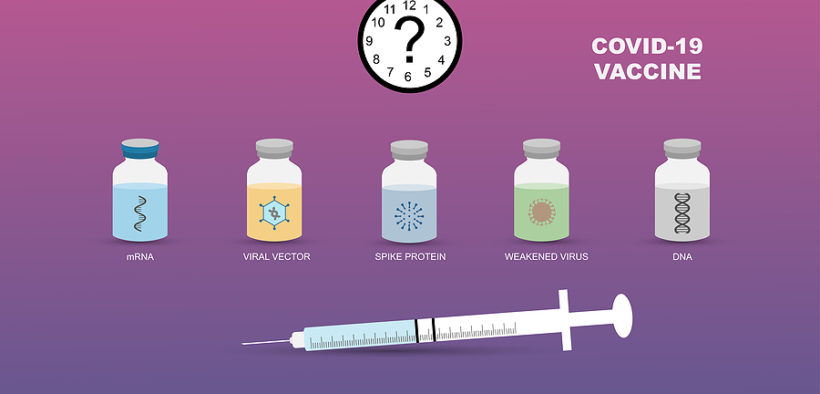
There are four main vaccines running in clinical trials for the coronavirus.
1. Whole Virus
A lot of conventional vaccine types utilize a whole virus to activate an immune response in the body. These include two approaches: Live attenuated vaccines and inactivated vaccines. The former ones contain an attenuated form of the virus which can be replicated without depicting any sign of illness. Inactivated vaccines utilize viruses that have genetic material destroyed, so these do not replicate but still might trigger an immune reaction in the body.
2. Protein Subunit
A protein subunit vaccine type has fragments of protein in them for triggering an immune reaction in the body. Doing the thing will reduce the risk of any side effects that are common in whole virus vaccines. However, the immune response produced might be weaker. It is the reason why these vaccines need adjuvants for helping to boost the immune response created by the body.
3. Viral Vector
Viral vector types also work by giving the cells genetic instructions to make antigens in the body. However, they might differ from the nucleic acid vaccines in the way that they use a virus that is harmless and is not like the one the vaccine will target in order to deliver the genetic instructions.
4. Nucleic Acid – DNA and RNA
These types of vaccines for the coronavirus utilize genetic material in the DNA or the RNA forms to give cells the instructions for making antigens. The viral spike protein is used in the case of the coronavirus. As the genetic material penetrates the body cells, it utilizes the protein factories of the cell to create an antigen for triggering an immune response in the body. The benefits of the vaccines will be that they are relatively easier to create and are affordable. The immune reaction is often strongly induced by these vaccines. All of these vaccines are in their trials as protective measures against the coronavirus. The efficacy of the vaccines is yet to be monitored.








